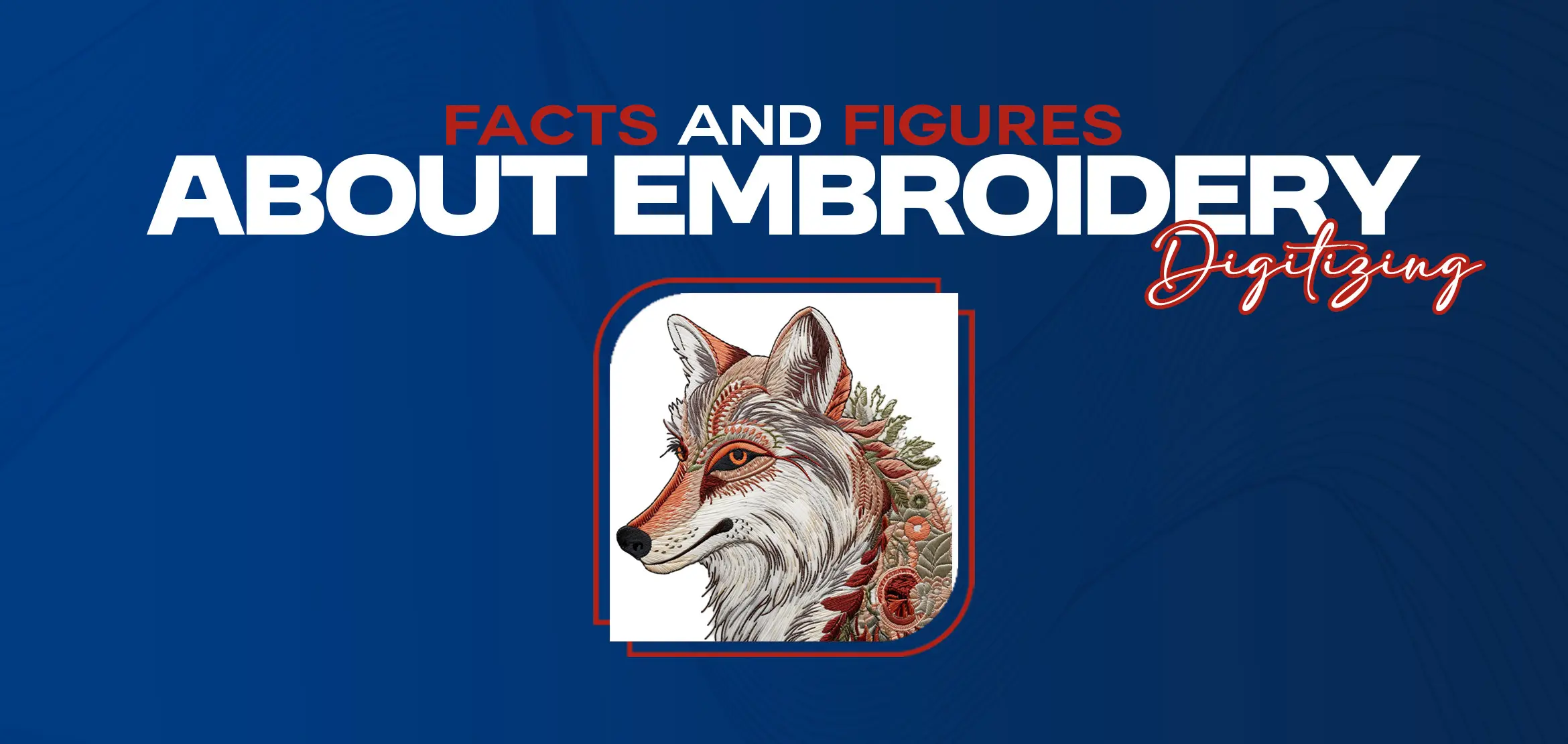
Is Embroidery digitizing hard?
Table Of Content
- Understanding the Differences Between Embroidery Digitizing and Digital Embroidery
- What is Embroidery Digitizing?
- What is Digital Embroidery?
- Choosing Between Digitizing and Digital Embroidery
- The Three Basic Methods of Transferring Embroidery Designs: Which One is Right for You?
- Tracing:
- Photocopying:
- Heat and Pressure:
- Exploring the Decline in Embroidery and Its Effect on the Industry
- The Future of Embroidery
- Reduced Stress and Anxiety
- Improved Hand-Eye Coordination and Dexterity
- Creativity and Self-Expression
- Cautions for Certain Medical Conditions
- Embroidery vs. Printing: Which One Lasts Longer?
- Three Types of Digitization: Which One Will Bring Your Designs to Life?
- 1: Manual Punching
- 2: Automatic Punching
- 3: Photo Digitizing
- Disadvantages of Digital Embroidery: What to Watch Out for When Using This Method
- 1: Expensive Equipment and Software
- 2: Limitations in Design Complexity
- 3: Maintenance and Upkeep
- Conclusion
Embroidery digitizing, like any new skill, can seem intimidating at first. However, with the right approach, tools, and techniques, it can be a rewarding endeavor that adds a unique touch to your clothing and accessories. In this post, we will explore the differences between digitizing embroidery and digital embroidery, the various methods of transferring embroidery designs, the health benefits of embroidery, and much more to help you determine if this hobby is right for you.
Let's begin!
Understanding the Differences Between Embroidery Digitizing and Digital Embroidery
Embroidery digitizing and digital embroidery are terms that are often used interchangeably, but they are actually two distinct processes with different requirements and outcomes. Here are some key differences:
What is Embroidery Digitizing?
Embroidery digitizing is the process of creating a digital embroidery file from a design. This involves taking an image or graphic and converting it into a series of commands that an embroidery machine can read and stitch onto fabric. This process requires specialized software and a skilled digitizer who can use the software to create the commands that will produce the desired design.
What is Digital Embroidery?
Digital embroidery, on the other hand, is the actual stitching of the design onto fabric using an embroidery machine. This process does not involve any manual input beyond loading the design file into the machine and setting it up for stitching. Digital embroidery is a streamlined and automated process that can produce high volumes of uniform designs quickly and efficiently with digitizing embroidery designs.
Choosing Between Digitizing and Digital Embroidery
Choosing between digitizing and digital embroidery depends on a number of factors, including the complexity of the design, the size of the order, and the available budget. For small runs or one-off custom designs, digitizing is often the best choice because it allows for greater design flexibility and precision. For larger orders or standardized designs, digital embroidery may be more cost-effective because it requires less manual labor and produces uniform results.
The Three Basic Methods of Transferring Embroidery Designs: Which One is Right for You?
Once you have a design for embroidery, you will need to transfer it onto the fabric you'll be stitching. There are three basic methods of transferring embroidery designs: tracing, photocopying, and using heat and pressure. Which one is right for you will depend on the complexity of your design, your budget, and the equipment you have available. Let's explore each method in more detail:
Tracing:
Vector Tracing or Tracing is the most traditional method of transferring embroidery designs. You'll need to have tracing paper, a tracing wheel, and a pen or pencil. Start by tracing the design onto the tracing paper with the wheel, making sure to transfer all of the details accurately. Then place the tracing paper onto the fabric, trace the design again with the wheel, and the ink from the pen or pencil will transfer onto the fabric.
Tracing is a low-cost method but can be time-consuming, especially for intricate designs. It also requires a steady hand and good eye for detail to ensure that the design is transferred accurately.
Photocopying:
Another method is to photocopy the design onto transfer paper and then iron it onto the fabric. This method is quicker than tracing, but you'll need access to a photocopier and transfer paper. Photocopying can also be more accurate than tracing, as you don't have to worry about any shaky hands or missed details. However, it may not be as suitable for very intricate designs.
Heat and Pressure:
This method involves using a heat press or an iron to transfer the design directly onto the fabric. You'll need to print the design onto transfer paper, place it onto the fabric, and then apply heat and pressure to transfer the design. This method is the quickest and easiest, but may not produce the highest quality results, especially for fine details.
Ultimately, the method you choose will depend on your personal preferences and the specific requirements of your design. Be sure to consider the complexity of your design, your budget, and the equipment you have available when choosing which method to use.
Exploring the Decline in Embroidery and Its Effect on the Industry
Embroidery has a long history dating back centuries, but in recent years there has been a decline in its popularity. One of the factors contributing to this decline is the rise of digital printing, which allows for faster, more cost-effective production of garments and other items.
Another factor is the availability of cheaper, mass-produced clothing that does not require the same level of customization or attention to detail that embroidering does. Consumers are also increasingly focused on convenience and speed, which isn't always served by embroidery.
Despite these challenges, embroidery still has a place in the market for high-end, customized items and personalized gifts. Embroidery can add value and exclusivity to a product or garment, making it stand out in a crowded marketplace.
To remain competitive, embroidery businesses must adapt to changing customer demands and explore new markets. For example, corporate branding and promotional products can be a profitable avenue for embroidery, as businesses often require customized items such as embroidered shirts, hats, bags, and more. Additionally, the trend towards sustainability and “slow fashion” could lead to growth in embroidery, as consumers increasingly seek out unique, handmade items that are produced in a more sustainable manner.
The Future of Embroidery
While embroidery may be facing challenges in the short term, it still has many potential applications and opportunities for growth in the long term. As technology continues to evolve, new methods and materials for embroidery may emerge, further extending the possibilities of this venerable art form.
It is ultimately up to embroidery businesses to adapt to changing customer demands and stay ahead of the curve when it comes to technology and innovation. Those that can successfully do so will be able to thrive despite the challenges facing the industry.
The Health Benefits of Embroidery: Is It a Good Hobby for You?
Embroidery is not only a fun and creative pastime, but it also has potential health benefits. Here are a few reasons why taking up embroidery might just be good for you:
Reduced Stress and Anxiety
Embroidery can be a therapeutic and relaxing activity that can help reduce stress and anxiety levels. The repetitive nature of the stitches can have a calming effect and promote a sense of mindfulness.
Improved Hand-Eye Coordination and Dexterity
Embroidery involves using your hands in a precise and coordinated way, which can help improve hand-eye coordination and dexterity. This is particularly beneficial for older adults who may be experiencing declines in these abilities.
Creativity and Self-Expression
Embroidery is an excellent way to express your creativity and individuality. Whether you are creating your own designs or customizing pre-made ones, embroidery offers limitless possibilities for personalization and self-expression.
Cautions for Certain Medical Conditions
While embroidery has many potential benefits, it may not be a suitable hobby for everyone. Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, may need to take caution and talk to their doctor before taking up embroidery. It's important to listen to your body and take breaks when needed to prevent injury.
Overall, embroidery is a fun and rewarding hobby that can also provide potential health benefits. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned pro, it's never too late to pick up a needle and thread and give embroidery a try.
Embroidery vs. Printing: Which One Lasts Longer?
When it comes to longevity, embroidery tends to last longer than printing. This is because embroidery involves stitching the design directly onto the fabric, rather than applying it as a layer like in printing.
Embroidery is also less prone to fading or peeling over time, making it a popular choice for durable and long-lasting items like uniforms, bags, and hats.
However, embroidery may not be as suitable for complex designs or large areas of coverage as printing can be. Additionally, embroidery can be a more expensive and time-consuming process than printing, as each design must be digitized and then stitched onto the fabric.
In summary, if you're looking for a long-lasting and durable option, embroidery may be the better choice. But if you have a complex design or need to print on a large area, printing may be the way to go.
Three Types of Digitization: Which One Will Bring Your Designs to Life?
Digitization is the process of translating a design into a digital embroidery file that can be read by an embroidery machine. There are three main types of digitization:
1: Manual Punching
Manual punching is a time-consuming process that involves manually inputting each stitch of the design into a digitizing software. This method produces the most precise results, making it an ideal choice for intricate designs and logos.
2: Automatic Punching
Automatic punching, on the other hand, uses software to convert an image or design into an embroidery file. Although faster than manual punching, this method may not be as accurate or suitable for complex designs.
3: Photo Digitizing
Photo digitizing involves scanning a physical image or design and converting it into an embroidery file using specialized software. This method can be a good option for reproducing logos or photographic images, but may not be suitable for highly detailed designs.
Choosing the right digitization method depends on the complexity and quality of the design, the quantity of items to be embroidered, and the budget for the project. It is important to work with a skilled digitizer who can advise on the best method for each specific project.
Disadvantages of Digital Embroidery: What to Watch Out for When Using This Method
Digital embroidery, while a useful and efficient method, does have its drawbacks. Here are some things to consider when using this method:
1: Expensive Equipment and Software
In order to perform digital embroidery, specialized equipment and software are necessary. This can be a costly investment, especially for small businesses or individuals just starting out in the industry.
2: Limitations in Design Complexity
Sometimes, the size and complexity of a design can exceed the capabilities of the equipment and software used for digital embroidery. This can limit the creativity and customization potential of the designs being produced.
3: Maintenance and Upkeep
Like any electronic equipment, digital embroidery machines require consistent maintenance and updates to function properly. This can be time-consuming and expensive.
It is important to weigh the pros and cons of digital embroidery before deciding to invest in this method, and to ensure that proper care is taken to maintain the equipment and software to maximize longevity and efficiency.
Conclusion
Embroidery digitizing can be a challenging process that requires specialized software and skills, but the end results can be breathtaking. With the decline in popularity of embroidery, businesses must adapt to changing customer needs and explore new markets to remain competitive. Embroidery has proven to have therapeutic benefits and can produce longer-lasting designs than printing. When choosing between digitizing and digital embroidery, factors such as budget, design complexity, and quantity of items should be taken into consideration. Ultimately, with the right tools and mindset, embroidery digitizing or custom embroidery digitizing is a satisfying and rewarding endeavor.